Trust in Carbon Credits
The global urgency to fund and scale climate mitigation activities, whether through compliance mechanisms such as Article 6 or the voluntary carbon markets, faces a fundamental obstacle: a pervasive lack of trust. Public confidence has eroded due to reports of inflated claims, high intermediary costs, and complex, opaque practices. These issues are deeply rooted in how climate impact claims are evaluated, certified, and monetised. The credibility and integrity of Measurement, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) processes form the backbone of environmental finance, yet traditional MRV systems have struggled to assure transparency and accountability. Decentralised digital MRV (D-MRV) offers a radical rethinking of this landscape.

Traditional MRV systems rely on centralised authorities to monitor, validate, and certify carbon reduction efforts. Such arrangements hinge on institutional reputations and proprietary methods, which too often remain hidden from public scrutiny. Inconsistent standards, along with occasional cases of mismanagement and fraud, have severely undermined public trust. The result is a climate finance ecosystem hobbled by suspicion and inefficiency, preventing the large-scale deployment of capital where it can deliver meaningful environmental and social benefits.
Welcoming WISP
Decentralising digital MRV eliminates the central points of failure that characterise legacy systems. Decentralised platforms shift verification processes into transparent, publicly auditable frameworks. These frameworks leverage emerging technologies—zero-knowledge proofs, cryptographic attestations, and advanced machine learning models—so that claims can be verified consistently, without over-reliance on any single intermediary’s integrity.
Several breakthrough innovations are converging to realize this vision. Web-based standards for verifiable claims, blockchain-based trust layers, and advanced AI techniques have come together on the IXO Spatial Web Platform. This platform integrates Giza’s Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning (ZKML) technology to deliver open, automated auditing processes that reinforce trust and reliability. A notable outcome of this collaboration is WISP, a specialised verification agent designed to evaluate and certify climate impact claims with precision and accountability.
Automating MRV
In a D-MRV architecture, claims originate as standardised, verifiable credentials. These credentials encode vital information about climate interventions, their geographic context, and their anticipated outcomes. Autonomous verification agents, referred to as Oracles in the IXO Spatial Web context, then apply machine learning models guided by Causal AI techniques to evaluate claims against established benchmarks and transparent criteria.

The World Wide Web Consortium’s verifiable claims standard ensures that the lineage and authenticity of all data points are cryptographically secure. The IXO Protocol leverages these standards so that claims can be validated, published, evaluated, and verified with cryptographic proofs. Verification outcomes are not merely trust-based assertions; they are systematically generated and signed by software agents. These agents use both rule-based logic and statistical inference, producing probabilistic assessments of a claim’s validity along with confidence levels and error margins. While no system is immune to occasional misclassifications, D-MRV allows methodologies to be tested and refined continuously, achieving performance thresholds that stakeholders can openly verify and adjust.
Autonomy to Self-Certify
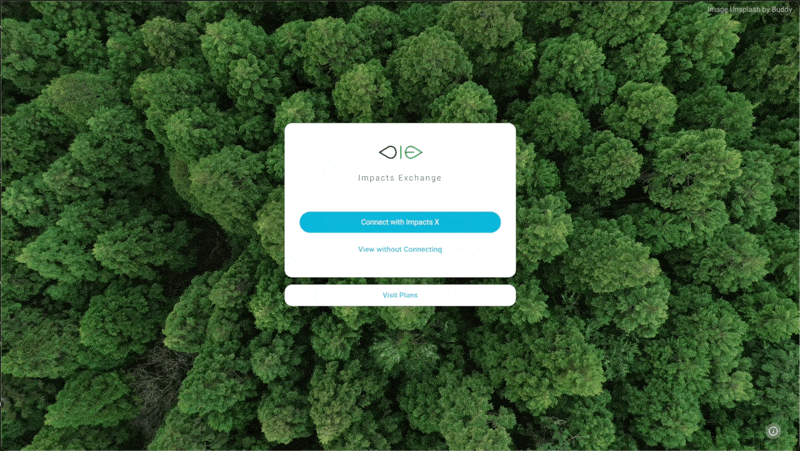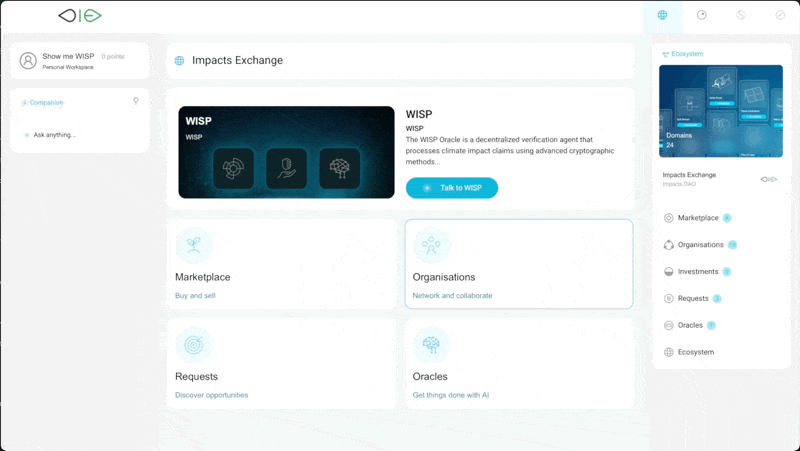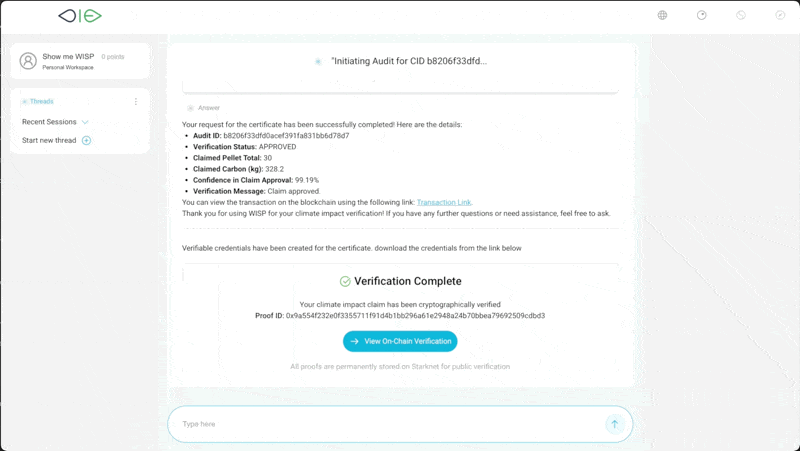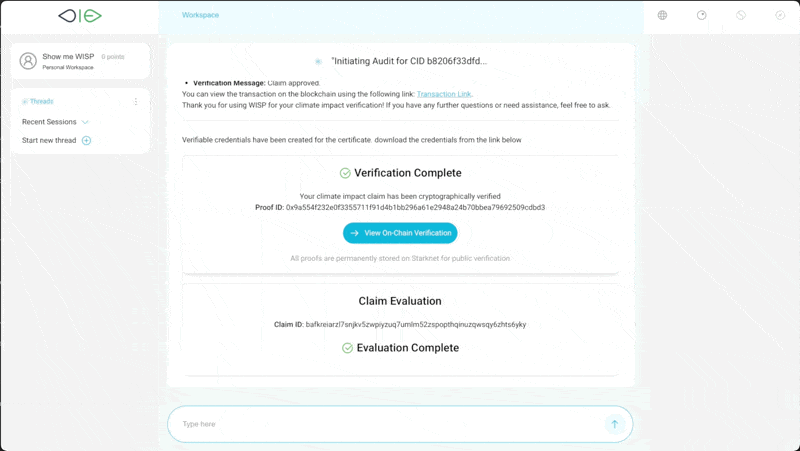
A defining feature of D-MRV is its capacity for claims to self-certify using autonomous verification services. Instead of depending on human auditors or centralised entities, software agents produce cryptographically signed verifiable credentials confirming the evaluation result. These results can be trusted without even necessarily revealing the Oracle implementer’s identity, as the process and code are transparent and verifiable – in the same way that most decentralised finance (deFi) services operate. This greatly enhances market fairness and accessibility, allowing even smaller projects or under-resourced actors to prove their impact credibly.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs
The D-MRV approach builds upon verifiable code execution, where computations and their results are guaranteed correct by design. Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) allow one party to prove a statement’s truth to another without disclosing underlying data, thus preserving confidentiality and privacy. In climate finance, this approach is invaluable since projects often handle sensitive data.
The integration of ZKP-based verification, exemplified by Giza’s services, ensures that every step of code execution is not only accurate but transparently evidenced. When a claim is evaluated, the model version and execution proof are recorded. This record can be replayed or audited by any independent operator, delivering a tamper-proof, traceable history of how conclusions were reached. Such openness encourages continuous improvement and cross-validation against other benchmark methodologies.
WISP, an agent built on these principles, integrates seamlessly with the IXO Spatial Web Platform and Giza’s verifiable execution services. WISP provides autonomous, evidence-based verdicts on the credibility of climate impact claims. Its operations are fully auditable and privacy-preserving, enabling a dynamic marketplace of verification services that compete on quality, speed, and cost—rather than relying on institutional gatekeepers.
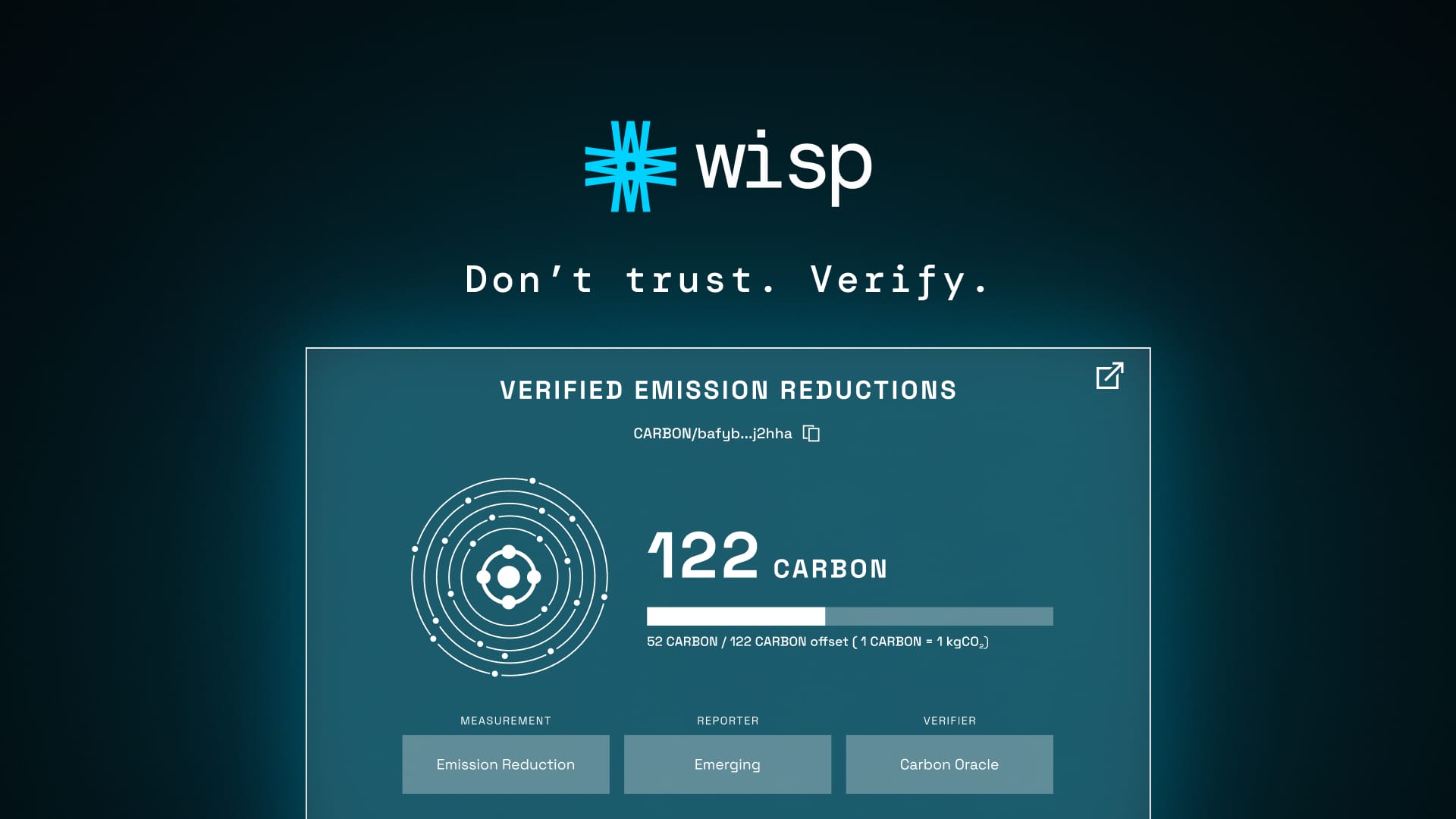
Don’t Trust, Verify
The decentralisation and digitisation of MRV redefine what it means to trust climate finance mechanisms. Instead of relying solely on the reputations of institutions or opaque assessments, investors, regulators, and citizens can now depend on transparent, mathematically verifiable proofs of claims. This not only restores confidence but significantly expands the capacity to channel funding toward high-quality climate interventions.

As the world confronts the escalating challenges of climate change, effective verification of environmental impacts is no longer optional. D-MRV, powered by agentic verification and advanced cryptographic methods, transcends the limitations of traditional systems. It provides a roadmap for evolving beyond trust deficits, inefficiencies, and reputational damage, making it possible for climate finance to finally operate at the speed and scale required to achieve global sustainability goals.
About IXO World
IXO World is a pioneer of the Internet of Impacts. Its Spatial Web Platform delivers advanced, intelligent operating systems to coordinate, finance, verify, govern, and inform real-world impact domains. Over the past decade, IXO World has set new standards for transparency, accountability, and innovation in the global sustainability landscape.
Connect with IXO World:

About Giza
Giza's WISP agent represents the cutting edge of verifiable AI systems for climate impact verification. Building on years of research in zero-knowledge machine learning and autonomous systems, Giza develops trustless infrastructure that enables the next generation of decentralized applications.
Connect with Giza: